Transformer is an electrical device whose main purpose is to transfer power from one electrical circuit to another circuit, but apart from this transformer is also a constant frequency, constant power and constant flux device. Transformer works on the principle of Faradays Law of electromagnetic Induction and it say that whenever there is a relative space or time variation between the magnetic field and the conductor an emf will be induced and in case of transformers the variation is in terms of time. Transformers are broadly divided into two types:
Power Transformer
Instrument Transformer
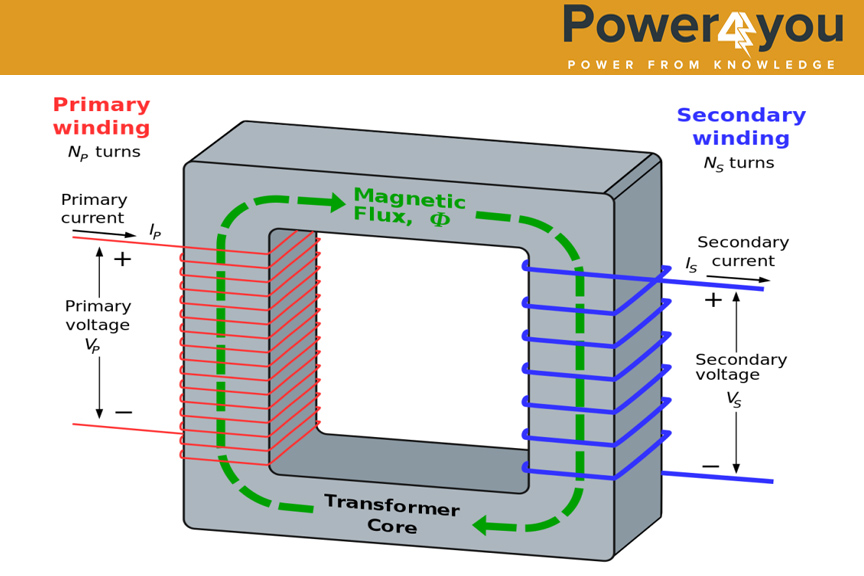
First of all we will discuss about the power transformers. In power transformers there is a core inside the casing and it has got two wingdings. one is called LV winding and the other one is called HV winding, it will be wrong if we say primary or secondary winding because until and unless the respective wingdings are connected to the source or load we can’t say which one is primary side and which one is secondary side. Below shows the winding connections in a single phase power transformer.
But in case of power plants we generally use three phase transformers. In case of three phase power transformers in both LV side and HV side it has got three terminals(R-Y-B).Let us discuss how the power is transferred from one circuit to another. When we connect the transformer to a source that particular winding is referred as the primary side and when the source is connected it draws the primary current Ip and this Ip creates a field in the core which is called main field and that main field induces secondary emf in the secondary winding and when the secondary winding is connected to a load it draws secondary current. This is how power is transferred from one circuit to another circuit. This is just an overview how power is being transferred from one circuit to another, but in actual depending on the No-load and Full-load conditions different types of operations take place.

Different Types of Power Transformers in Thermal Power Plant:
- Generator Transformer
- Station Transformer
- Unit Auxiliary Transformer
- Excitation Transformer
- Unit Service Transformer
- Generator Transformer
It is the transformer which is connected directly to the generator and it is always a step-up transformer.it steps-up the voltage level of the generator to a higher value matching the grid voltage. The reason it is always a step-up transformer is that the generation voltage for the generator we are always keeping it low due to the restrictions on Insulation damage.
- Station Transformer
It is always a step-down transformer and it takes the supply from the grid and gives to the unit auxiliaries.it is mainly used in case of start-up of the Unit or during power outage from the generator.
- Unit Auxiliary Transformer
It is also a step-down transformer and it takes the supply from the generator output terminal and supplies to the auxiliaries for running various equipments in the plant and it directly feeds the HT line.
- Excitation Transformer
As the name signifies it is mainly used for providing electrical supply for excitation to the generator rotor winding. It takes the supply from the generator output terminals and steps it down to a lower voltage suitable for the excitation
- Unit Service Transformer
The work of the Unit Service transformer is to step-down the voltage level for suppling the LT line and it takes the supply from the HT line. It is basically a step-down transformer
Coming to the instrument transformers there are different types of Instrument transformers:
There are mainly two types of instrument transformers used in power plants,one is CT (Current Transformer) and the other one is PT (Potential Transformer).The work of the PT is to measure the Voltage of High Voltage lines and the work of the CT is to measure the current level, but in case of CT they are used in two ways, one for measuring and protecting.

(Current Transformer)

(Potential Transformer)
If you see a CT or a PT,then they both will look alike.The only difference between a CT and a PT is that CT is connected in series and PT is connected in parallel.